Architecture

Prerequisites
- Have a AWS CLI configured with admin permission to create resources and launch the CDK stack
- Have AWS git-remote-codecommit setup with your account to be able to interact with the CodeCommit repository in your account
- Have Snyk token and Snyk Org ID available to you on AWS SSM Parameter store in your AWS account
Setting up the environment
1. Creating AWS CodeCommit repository
Before starting this section, make sure you have a CodeCommit repository created in your AWS account. Once the CodeCommit repository is created, we will be commiting two scripts needed for the build environment to create a requirements.txt. These scripts are located here
To create a new CodeCommit repository using AWS CLI , run the following command.
> Ensure you have codecommit:CreateRepository permission for your user profile
aws codecommit create-repository --repository-name SnykCodeArtifactRepo --repository-description "Snyk CodeArtifact repo"Once the repository is successfully created you will see a message like the one below
{
"repositoryMetadata": {
"accountId": "112233445566",
"repositoryId": "c4721f38-61c2-4143-8a64-d46486deea1b",
"repositoryName": "SnykCodeArtifactRepo",
"repositoryDescription": "Snyk CodeArtifact repo",
"lastModifiedDate": 1620395170.604,
"creationDate": 1620395170.604,
"cloneUrlHttp": "https://git-codecommit.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/v1/repos/SnykCodeArtifactRepo",
"cloneUrlSsh": "ssh://git-codecommit.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/v1/repos/SnykCodeArtifactRepo",
"Arn": "arn:aws:codecommit:us-east-1:112233445566:SnykCodeArtifactRepo"
}
}Copy the Arn, and cloneUrlHttp fields in a separate place for usage later in the deployment stage
2. Setting up CodeCommit Repo
Once the repository has been created, 2 scripts have to be uploaded to the repo prior to kicking off the deployment of the CDK stack. Both of these scripts are located under the workshop-resources\scripts\ directory. The list_repos.py script queries the CodeArtifact domain for all packages and their default display version and writes it to a requirements.txt file, the pip_install.py script manually steps through each pip install command to ensure any failures are graceful and recorded for the DevSecOps engineer to identify. Both of these files can be manually uploaded to codecommit through the AWS Console. See here for instructions on uploading files to AWS CodeCommit.
3. Creating AWS CodeArtifact Domain and Repository
To Create a new CodeArtifact Domain and repository using CLI, run the following commands:
aws codeartifact create-domain --domain demo-domainNote that the --domain must be numbers & lowercase letters only. You should see a message like below on a successful creation:
{
"domain": {
"name": "demo-domain",
"owner": "112233445566",
"arn": "arn:aws:codeartifact:us-east-1:112233445566:domain/demo-domain",
"status": "Active",
"createdTime": 1620397725.902,
"encryptionKey": "arn:aws:kms:us-east-1:112233445566:key/72224f64-5f1e-4a16-ac69-398ff25b8617",
"repositoryCount": 0,
"assetSizeBytes": 0,
"s3BucketArn": "arn:aws:s3:::assets-193858265520-us-east-1"
}
}Note down the name & owner from the response as these will be used in the deployment stage.
Now that the domain is created, you can create a repository within that domain. Run the following:
aws codeartifact create-repository --domain demo-domain --repository pypi-storeThe above command should return a response like below
{
"repository": {
"name": "pypi-store",
"administratorAccount": "112233445566",
"domainName": "demo-domain",
"domainOwner": "112233445566",
"arn": "arn:aws:codeartifact:us-east-1:112233445566:repository/demo-domain/pypi-store",
"upstreams": [],
"externalConnections": []
}
}4. Associating CodeArtifact domain with external connection
The next step is associating the repository with an external connection. There are several external repositories available as external connections, but for this workshop we will be utilizing the Python Package Index public:pypi. To add this external connection run:
aws codeartifact associate-external-connection --external-connection public:pypi \
--domain demo-domain --domain-owner 112233445566 --repository pypi-storeWhich should return a response like below:
{
"repository": {
"name": "pypi-store",
"administratorAccount": "112233445566",
"domainName": "demo-domain",
"domainOwner": "112233445566",
"arn": "arn:aws:codeartifact:us-east-1:112233445566:repository/demo-domain/pypi-store",
"upstreams": [],
"externalConnections": [
{
"externalConnectionName": "public:pypi",
"packageFormat": "pypi",
"status": "AVAILABLE"
}
]
}
}This repository created will be the source for the Codepipeline that runs the Snyk CodeArtifact scan. The CodePipeline triggers daily and builds a requirements.txt file by listing the packages in CodeArtifact domain.
5. Populating the new repository
Now that your codeartifact repository has been set up. You need to configure your cli to pull packages using it. To do this, log into the AWS Management Console and navigate to CodeArtifact and locate your repository
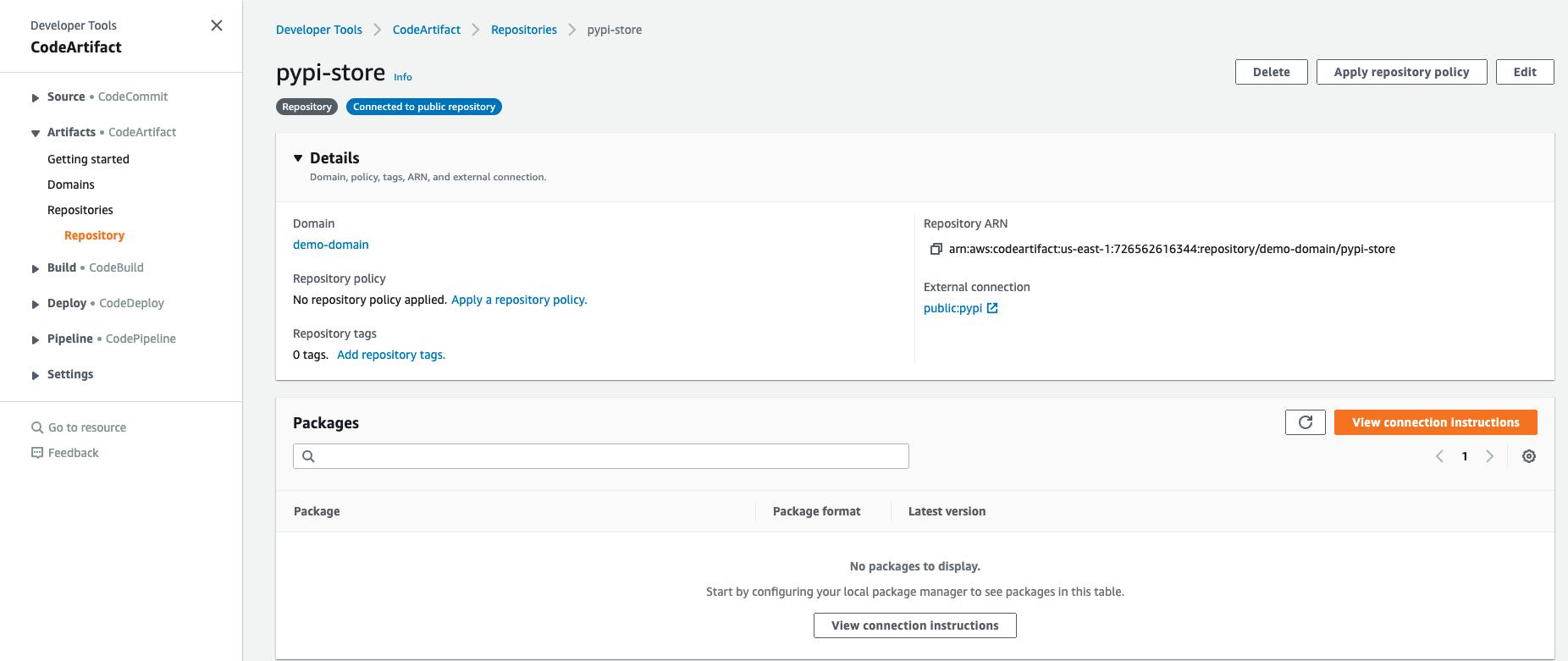
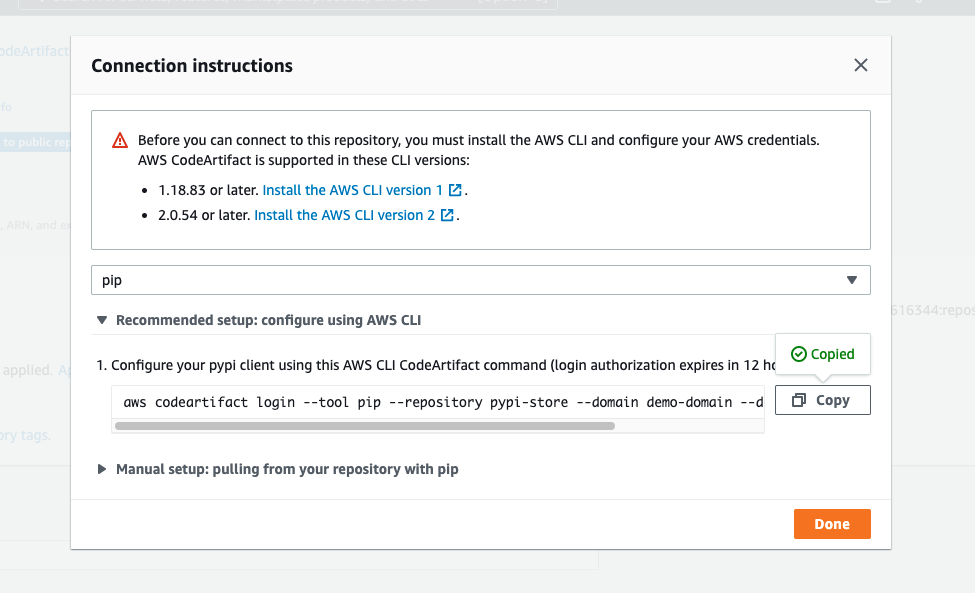
Click on the View connection instructions button and copy down the connection instructtions listed for pip as the package manager
In order to preserve your current python environment, create a local virtual virtual environment for python. To manually create a virtualenv on MacOS and Linux:
$ python3 -m venv .envAfter the init process completes and the virtualenv is created, you can use the following step to activate your virtualenv.
$ source .env/bin/activateIf youre on a windows platform, you would activate the virtualenv like this:
% .env\Scripts\activate.batOnce the virtualenv is activated, you can then install dependencies with pip. Log in to the codeartifact repository with the command copied from the console in the above steps
code aws codeartifact login --tool pip --repository pypi-store --domain demo-domain --domain-owner 112233445566You should receive the response:
Successfully configured pip to use AWS CodeArtifact repository https://demo-domain-112233445566.d.codeartifact.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/pypi/pypi-store/
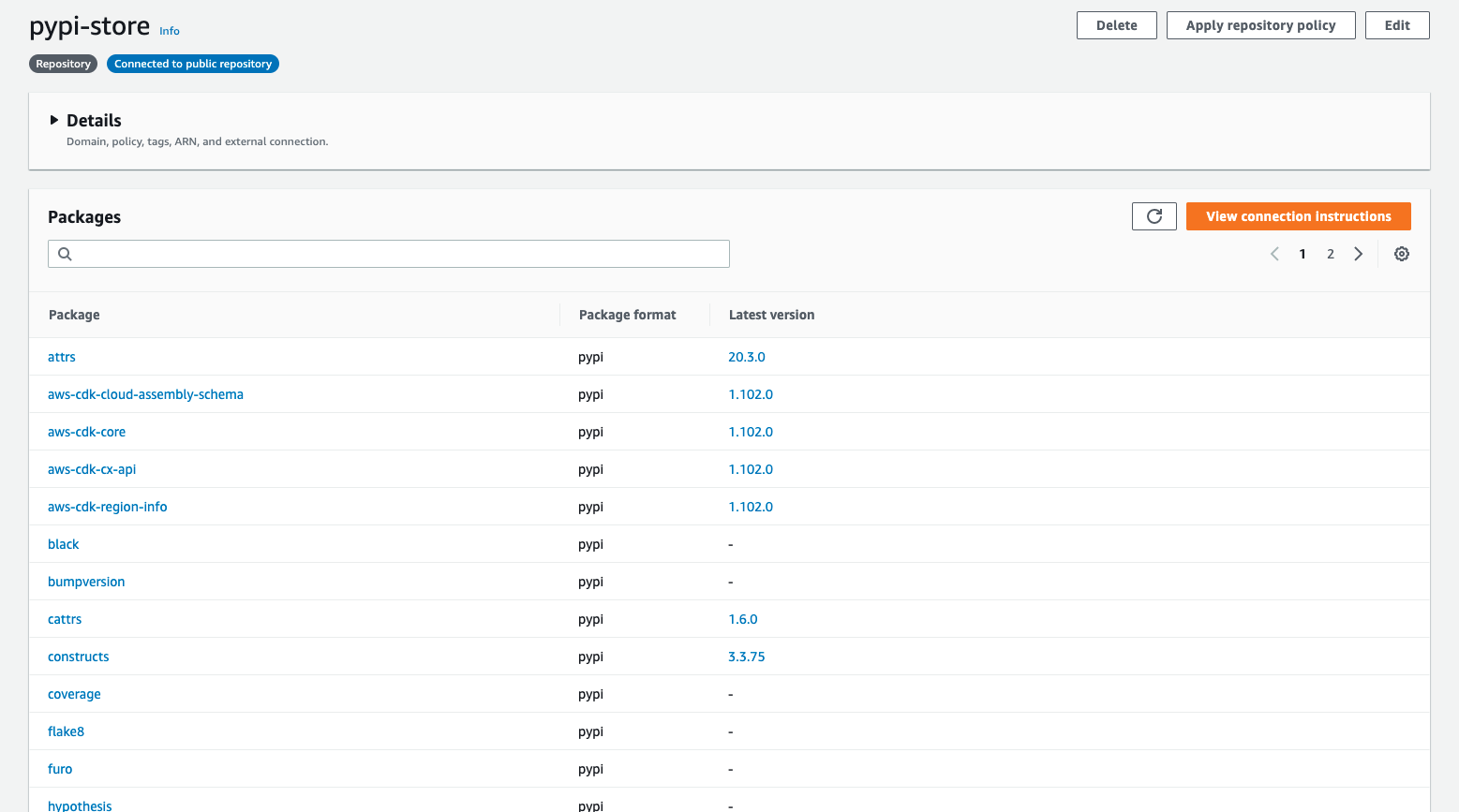
Login expires in 12 hours at 2021-05-07 23:58:57-04:00With the repository configured, run pip install aws-cdk.core to pull down some packages into the repository. If you navigate back into the CodeArtifact console, you will see that there are now multiple packages in the repository
6. Setting up CDK
To Deploy the cdk resources, clone down the workshop github. Navigate to workshop-resources/cdk/snyk-codesuite-cdk. Once in the repo initialize the virtual env and run
pip install -r requirements.txtSet your AWS Credentials in the CLI then navigate to the file located at workshop-resources/cdk/snyk-codesuite-cdk/cdk_stack_deploy/cdk_snyk_codeartifact_stack.pyand fill in the required parameters saved from previous steps.
Log into the AWS console or use the CLI to create 2 new parameters that the Codebuild job references. For steps on creating the parameter, use this link .
Once those are created and the parameters filed out in the CDK file, the stack can be deployed by running
cdk deploy cdk-snyk-ca-stackChecking results in S3
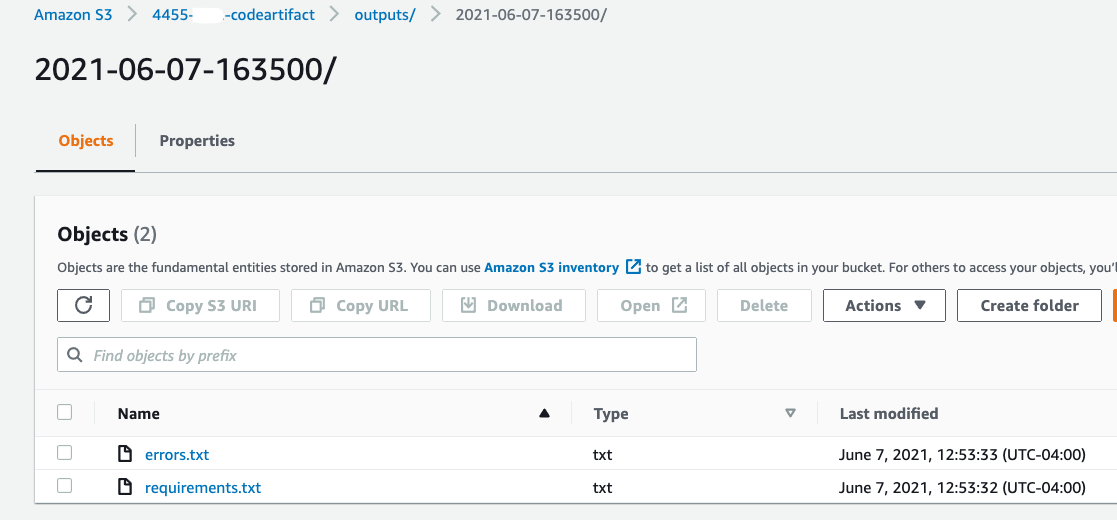
After the CodePipeline successfully runs and the build job is completed you should have results in the output section of the S3 bucket as well as in the Snyk Console. Let’s start with the S3 ouput as this is the raw build output. Under the bucket created in the stack which can be found in the resources section of the Cloudformation stack, navigate to the artifactbucket\outputs\ subfolder and locate the folder that matches the date & time of the last build project that ran. The build outputs two files, one with the requirements.txt file generated from the AWS CodeArtifact domain and the other a list of packages which could not successfully be installed by pip and therefore unable to be scanned by the Snyk CLI (These packages can be analyzed for incompatibilities such as python versions etc.)
Checking results in Snyk
After the build successfully runs, the Snyk console will generate a project with the name provided in the CDK definition during deployment. Navigate to the project in the the Snyk Console by clicking on it.

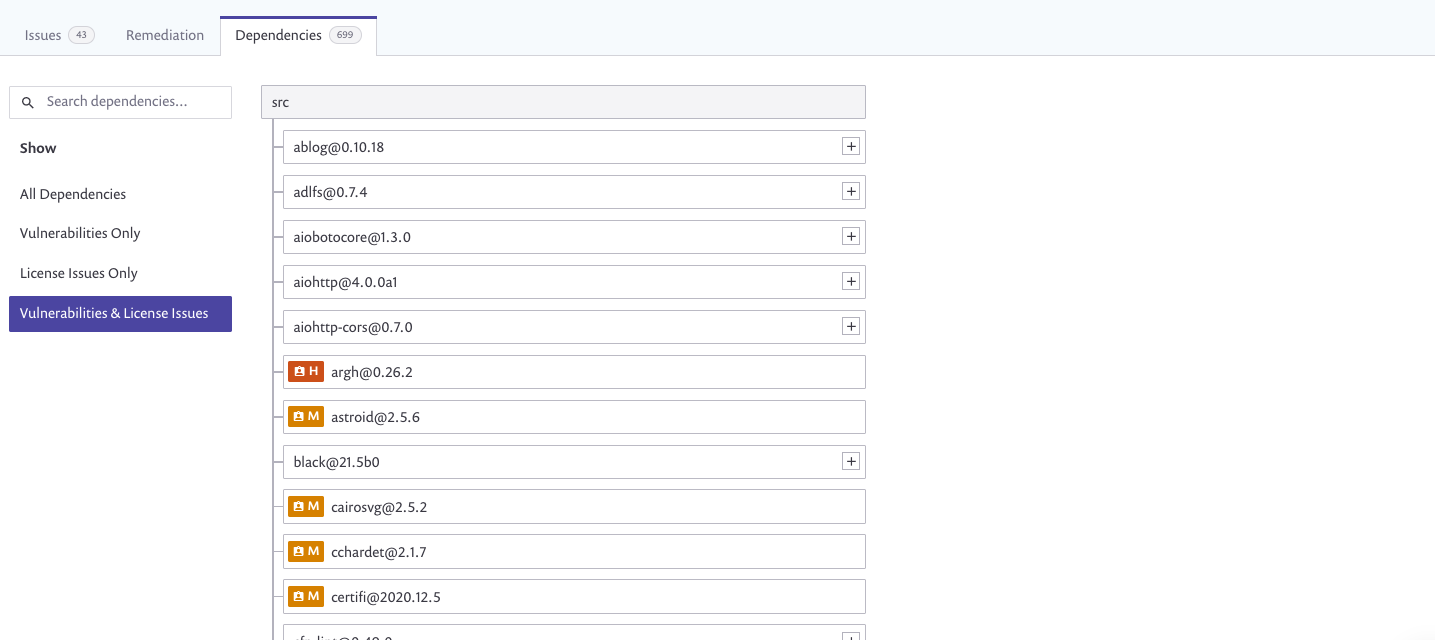
The project page will give you an overview of all the CodeArtifact domain including all the Dependencies, Issues(Both Vulnerability & License) as well as remediation informations for the vulnerabilities with a published fix.
Cleanup
As this lab creates resources which will accrue cost if not deleted, please run the following commands to cleanup the resources in this lab.
cdk destroyAfter the CDK stack has been destroyed, move onto deleting the CodeCommit repository using AWS CLI command
aws codecommit delete-repository --repository-name SnykCodeArtifactRepoFinaly we can delete the CodeArtifact Domain & Repository created
aws codeartifact delete-repository --repository-name SnykCodeArtifactRepo --domain demo-domainaws codeartifact delete-domain --domain demo-domain